Vaccination Efforts
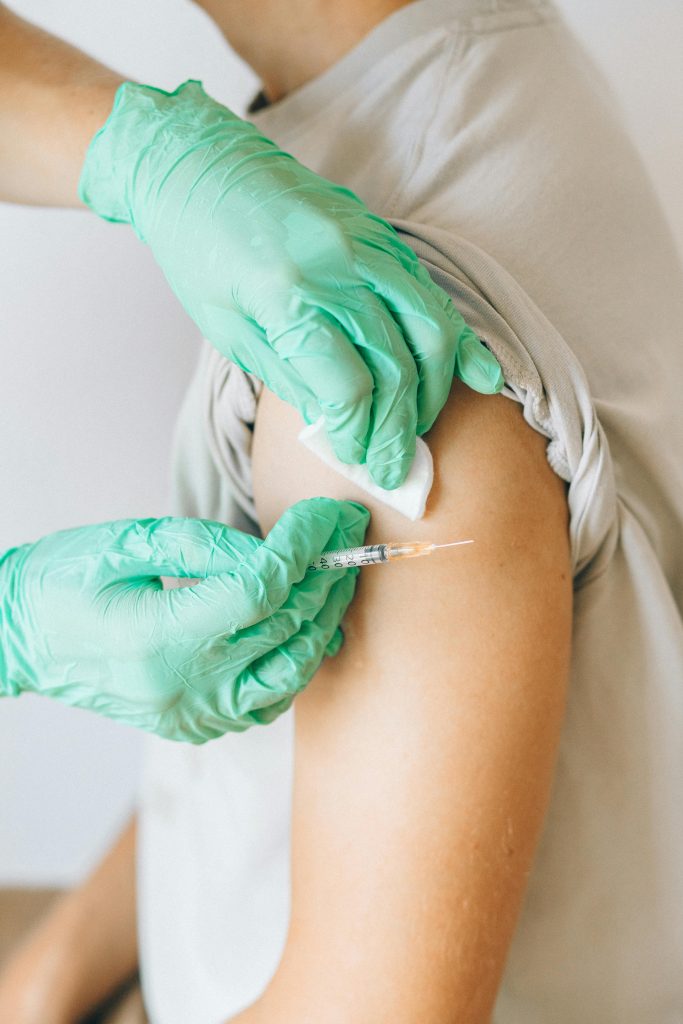
Vaccination remains one of the most cost-effective public health interventions, preventing millions of deaths each year. Recent global efforts have focused not only on sustaining high coverage for routine childhood immunizations but also on deploying new vaccines, addressing COVID-19 booster needs, and overcoming hesitancy to ensure equitable access. Global Immunization Coverage and Progress In 2023, an estimated 14.5 million “zero-dose” children, those who received no routine vaccines were identified, underscoring persistent gaps in reaching vulnerable populations. Coverage for the third dose of diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis (DTP3) vaccine stood at 84 %, while the first dose of measles vaccine reached 83 %, both still below pre-pandemic levels of around 86 % World Health Organization (WHO)World Health Organization (WHO). Despite challenges, global initiatives have saved an estimated 154 million lives over the past 50 years through coordinated immunization campaigns World Health Organization (WHO). COVID-19 Booster Campaigns Evolve As SARS-CoV-2 variants continue to circulate, many countries have adapted their booster recommendations. In May 2025, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) affirmed that clinical guidance and schedules for COVID-19 vaccines remain largely unchanged, while focusing updated compositions on high-risk groups CDC. Advisory discussions in April 2025 considered narrowing booster eligibility to vulnerable populations (e.g., elderly, immunocompromised) for the 2025–2026 season, aiming to balance protection with resource allocation Reuters. Deployment of New Vaccines: RSV and Malaria RSV Vaccines: After FDA approval in June 2024 for GSK’s Arexvy in adults aged 50–59 years, and earlier approvals for Pfizer’s Abrysvo in those 60+, RSV immunization is now an option for older adults at increased risk of severe respiratory disease CDCPfizer. Moderna’s mResVIA mRNA RSV vaccine, approved in late 2024, further expands choices for those 60 and older, with rollouts underway in multiple regions CDC.Malaria Vaccines: In January 2024, the WHO’s AMVIRA initiative began scaling up malaria vaccine introductions across 17 endemic African countries, bolstering programs delivering the RTS,S/AS01 (Mosquirix) and R21/Matrix-M vaccines to children in high-transmission zones World Health Organization (WHO)World Health Organization (WHO). Reinvigorating Routine Immunization The 2024 Global Vaccine Market Report highlights that 88 vaccine products were distributed across 207 countries, yet service disruptions during the COVID-19 pandemic caused 67 million children to miss at least one dose between 2020–2022 World Health Organization (WHO)UNICEF. Efforts to restore routine coverage include integrated outreach campaigns combining childhood immunizations with nutrition and deworming services, particularly in low-resource and conflict-affected areas. Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy and Equity Confidence in vaccines declined in several regions during the pandemic, with some countries seeing up to a 44 percentage-point drop in trust for routine childhood vaccines UNICEF. To counter this, community-based education, engagement of local leaders, and transparent communication about safety and efficacy have been prioritized. Expanding broadband access and mobile-health platforms also supports remote appointment scheduling and follow-up reminders, helping reduce missed opportunities. Digital Strategies Strengthen Campaigns The TAG-CO-VAC meeting in May 2025 called for standardized data sharing on vaccine antigen composition, urging manufacturers to publish immunogenicity and variant-coverage data to inform global decisions World Health Organization (WHO). The WHO’s Immunization Data Portal provides real-time dashboards on vaccine-preventable disease trends, equipping policymakers with insights to target resources where gaps are greatest Immunization Data. Challenges and Future Outlook Key challenges include ensuring sustainable financing, harmonizing regulatory pathways for new vaccines, and safeguarding cold-chain integrity in remote regions. The Global Strategy for Immunization 2025–2030 emphasizes multisectoral collaboration, workforce development, and leveraging digital tools for surveillance and outreach. Continued investment and policy support will be critical to achieving Universal Health Coverage goals and ensuring that “no one is left behind.” ConclusionRecent vaccination efforts demonstrate a dual focus on restoring routine immunization to pre-pandemic levels and integrating new vaccine technologies for RSV, malaria, and COVID-19 boosters. By combining evidence-based campaigns with targeted digital strategies and community engagement, global health systems are better positioned to protect all age groups, especially the most vulnerable from vaccine-preventable diseases.
Mental Health Awareness

Mental health awareness has gained unprecedented global momentum, driven by concerted advocacy, policy reforms, and innovative technologies. From high-profile campaigns to groundbreaking digital solutions, efforts to destigmatize mental illness and improve access to care are reshaping healthcare landscapes worldwide. Global Prevalence and Burden An estimated 970 million people worldwide were living with a mental health condition in 2019, with anxiety and depression the most common disorders World Health Organization (WHO). Mental health conditions account for a growing share of the global disease burden, representing one in eight of all health conditions and contributing substantially to disability and lost productivity World Health Organization (WHO). Awareness Campaigns and Initiatives World Mental Health Day Held every October 10, World Mental Health Day unites stakeholders to spotlight mental health and combat stigma. The 2024 theme, “It Is Time to Prioritize Mental Health in the Workplace,” engaged employers and employees globally in fostering supportive work environments wmhdofficial.com. Viral Challenges and Grassroots Movements Social media challenges have been repurposed to raise both funds and dialogue. In early May 2025, the Ice Bucket Challenge resurfaced, this time to support Active Minds and encourage open conversations about mental health among youth raising over USD 345,000 within days Cadena SER. Technological Innovations: Digital Tools & Telepsychiatry Digital mental health apps numbered over 337,000 in 2024, with many focused on symptom tracking, self-guided therapy, and peer support IQVIA. The global mental health apps market was valued at USD 7.48 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a 14.6 % CAGR through 2030 Grand View Research. Telepsychiatry, a subset of telemedicine addressed a USD 9.9 billion market in 2023 and is forecast to expand at a 16.8 % CAGR through 2032 Global Market Insights Inc.. These services enable remote consultations, fostering continuity of care for those in underserved regions and reducing travel burdens for patients. Integration into Healthcare Systems In March 2025, the WHO released new guidance urging countries to transform mental health policies and integrate community-based services, highlighting that up to 90 % of those with severe mental disorders in some regions receive no care World Health Organization (WHO). The WHO Special Initiative for Mental Health aims to support low- and middle-income countries in scaling up services, targeting a one-in-eight global prevalence by strengthening policy, financing, and workforce capacity World Health Organization (WHO). Improving Access and Equity Digital platforms are narrowing gaps in care: 80 % of surveyed Americans support remote monitoring, and 88 % have accessed telehealth services in the past year Market.us Media. However, ensuring equitable access demands overcoming the digital divide expanding broadband infrastructure, designing intuitive user interfaces, and providing culturally tailored resources to reach marginalized and rural populations. Practical Applications in Special Populations Schools and workplaces increasingly embed mental health programs: online resilience training for students, stress-management webinars for employees, and peer-support chatbots for frontline workers. Teletherapy platforms have been adopted by universities and large employers to provide confidential, on-demand counseling, improving early intervention and reducing stigma within communities. Challenges and Future Directions Key challenges include ensuring data privacy, standardizing quality across thousands of digital tools, and developing sustainable reimbursement models. Despite surging venture capital—digital mental health saw a tenfold funding increase over the past decade, rigorous evaluation and regulatory oversight remain critical to validate efficacy and safety Reagan-Udall Foundation. Looking ahead, the WHO’s Comprehensive Mental Health Action Plan 2013–2030 and national strategies emphasize multisectoral collaboration, digital literacy training for providers, and ongoing monitoring to refine interventions based on real-world outcomes. ConclusionGlobal momentum in mental health awareness is fueled by powerful advocacy campaigns, rapid technological innovation, and evolving policy frameworks. To sustain progress, stakeholders must prioritize equitable access, robust evaluation, and community engagement ensuring mental health care is as accessible and integrated as any other essential health service.
Digital Health and Telemedicine
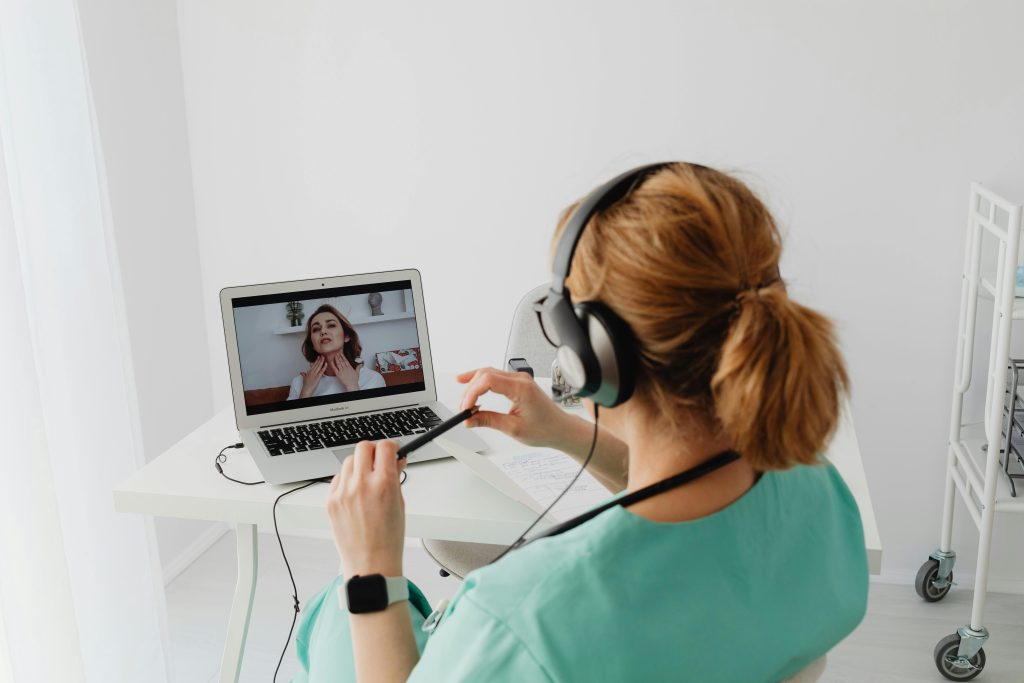

Digital health and telemedicine have rapidly evolved from niche services into integral components of healthcare delivery worldwide. Spurred by advancements in technology and driven by the need for more accessible, efficient care, these tools are transforming how patients and providers interact. This update aligns with the accessible, care-focused tone found on the Rehoboth Care Homes website, highlighting global trends, practical applications, and the impact on patient outcomes. Global Market Growth and Investment The global digital health market is projected to grow from USD 271.53 billion in 2024 to USD 319.16 billion in 2025, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.5 % The Business Research Company. Meanwhile, the telemedicine segment alone is expected to expand from USD 83.23 billion in 2024 to over USD 618 billion by 2033, with a 24.96 % CAGR through 2030 GlobeNewswire. This surge reflects increased investment by governments and the private sector, recognizing digital health’s role in reducing costs and increasing system resilience. Technological Innovations: AI, IoMT, and Wearables Artificial intelligence (AI) is at the forefront of innovation, optimizing workflows, powering diagnostic algorithms, and enabling personalized care plans. By 2025, healthcare AI spending is predicted to exceed USD 19 billion, growing at over 38 % annually Rural HealthBCG Global. Concurrently, the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) including connected devices like smart inhalers and glucose monitors is driving real-time health monitoring. Wearables, from fitness trackers to advanced health sensors, are increasingly integrated into telemedicine platforms, augmenting remote assessment and preventative care. Hybrid Care Models and Virtual Hospitals The rise of hybrid care models—combining in-person visits with virtual consultations—offers patients flexible pathways to care. Virtual hospitals, such as Seha Virtual Hospital in Saudi Arabia, now coordinate with hundreds of facilities to provide 44 specialized services remotely, improving outcomes in chronic disease management and post-operative care Financial Times. These “virtual hospitals” reduce travel burdens, lower per-patient costs, and enable specialist access for rural and underserved populations. Integration into Healthcare Systems Large-scale integration of telemedicine into national health systems has been guided by initiatives like the WHO’s “Support tool to strengthen telemedicine,” released in July 2024 World Health Organization (WHO). Regional bodies such as the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) emphasize telehealth’s role in equitable access, particularly during public health emergencies Pan American Health Organization. These frameworks help standardize quality, ensure interoperability, and foster provider training. Improving Access and Equity Digital health technologies are narrowing healthcare disparities. Telemedicine connects remote patients with specialists, eliminating geographic barriers and reducing travel-related strain on elderly or mobility-limited individuals JHU Bloomberg School of Public Health. However, to fully realize this potential, addressing the digital divide remains critical. Expanded broadband access, user-friendly interfaces, and culturally adapted content are essential to ensuring inclusive care World Health Organization (WHO). Practical Applications in Chronic Disease Management Telemedicine has demonstrated particular strength in chronic disease care, enabling regular follow-up and proactive interventions. Programs monitoring hypertension, diabetes, and heart failure remotely report improved adherence and reduced hospital readmissions JHU Bloomberg School of Public Health. Virtual care also supports mental health services, with telepsychiatry platforms offering timely counseling and crisis intervention, a boon for patients in areas with mental health professional shortages. Challenges and Future Outlook Despite its promise, digital health faces challenges: data privacy and security concerns, varying regulatory landscapes, and the need for robust reimbursement models. As AI-driven tools grow more complex, transparent validation and ethical guidelines will be vital. Looking ahead, the WHO’s Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020–2025 provides a roadmap for sustainable implementation, emphasizing policy alignment, workforce development, and continuous evaluation World Health Organization (WHO)World Health Organization (WHO). ConclusionDigital health and telemedicine are reshaping healthcare delivery on a global scale, offering scalable solutions to improve access, quality, and cost-effectiveness. By embracing AI innovations, expanding hybrid care models, and ensuring equitable access, healthcare systems can better serve all populations, including the elderly and chronically ill while maintaining the personal, compassionate care exemplified by Rehoboth Care Homes.
Healthcare News: Advancements, Trends, and Insights

Cutting-edge Medical Breakthroughs: Researchers have made significant strides in various areas of medicine. A groundbreaking study has shown promising results in gene therapy, offering potential cures for previously incurable genetic diseases. In addition, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning. Precision Medicine: Precision medicine has gained momentum, tailoring treatment plans to individual patients based on their genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environmental factors. This personalized approach holds great promise for improving patient outcomes, minimizing adverse reactions, and optimizing healthcare resource allocation.

